Measles
There has been a recent rise in measles cases in the UK (Dec 2023). Measles is spread when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can spread very easily.
You can protect your child by making sure they get 2 doses of the MMR vaccine. Normally the 1st is given at 12 months and the 2nd around 3 years 5 months old. Even if you or your children have missed these vaccines, it’s not too late to get them. Contact your GP practice today.
If your child has had both doses of their MMR vaccine, there is almost no chance of them getting measles (unless they have a severely weakened immune system).
There is more information about the MMR vaccine and other childhood vaccinations.
Measles can make some people very ill and can lead to severe complications
Click below to listen to a radio interview on measles with Dr Darren Ranasinghe, SWL Healthier Together Clinical Lead, and Dr Simon Drysdale, Paediatric Infectious Disease Consultant at St. George's Hospital:
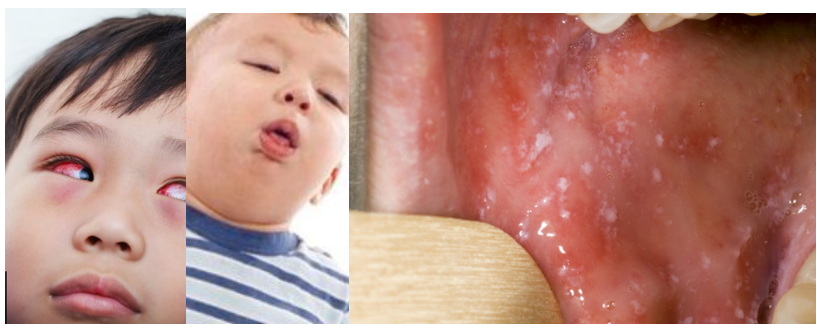
What are the symptoms of Measles?
Measles starts with:
● fever
● red, sore, watery eyes (conjunctivitis)
● runny nose
● cough



(image courtesy of www.blackandbrownskin.co.uk)
After a few days:
● Small white spots may appear inside their mouth and on the back of their lips
● A rash. The rash starts on the face and behind the ears. It then spreads all over the body. The spots of the measles rash are sometimes raised and often join together to form blotchy patches. They are not usually itchy. The rash looks brown or red on white skin. It may be more difficult to see on brown or black skin.
If your child has any of the following features:
- Breathing very fast, too breathless to talk, eat or drink
- Working hard to breathe, drawing in of the muscles below the ribs, or noisy breathing (grunting)
- Breathing that stops or pauses
- Is pale, blue, mottled or feels unusually cold to touch
- Difficult to wake up, very sleepy or confused
- Weak, high-pitched cry or can’t be settled
- Has a fit (seizure)
- Has a rash that does not go away with pressure (the ‘Glass Test’)
- Is under 3 months old with temperature more than 38°C or under 36°C (unless fever in the 48 hours following vaccinations and no other red features)
You need urgent help.
Go to the nearest Hospital Emergency (A&E) Department or phone 999. Let them know as soon as you arrive if your child has not been vaccinated against measles (MMR vaccine).
If your child has any of the following features:
- Breathing a bit faster than normal or working a bit harder to breathe
- Dry skin, lips or tongue
- Not had a wee or wet nappy in last 8 hours
- Poor feeding in babies (less than half of their usual amount)
- Irritable (unable to settle them with toys, TV, food or hugs even after their fever has come down)
- Is 3-6 months old with temperature 39°C or above (unless fever in the 48 hours following vaccinations and no other red or amber features)
- Temperature of 38°C or above for more than 5 days or shivering with fever (rigors)
- Temperature less than 36°C in those over 3 months
- Getting worse or you are worried about them
You need to contact a doctor or nurse today.
Please ring your GP surgery or call NHS 111 - dial 111
If symptoms persist for 4 hours or more and you have not been able to speak to either a member of staff from your GP practice or to NHS 111 staff, recheck that your child has not developed any red features.
If none of the above features are present
- Watch them closely for any change and look out for any red or amber symptoms
- If your child has any other symptoms associated with their fever, you may want to look at the information on sore throat, cough, earache, diarrhoea and vomiting or tummy ache or our other pathways.
- Additional advice is also available to young families for coping with crying of well babies.
Self care
Continue providing your child’s care at home. If you are still concerned about your child, speak to your health visitor, local pharmacist or call NHS 111– dial 111
Your child cannot go back to school or nursery until at least 4 days after the onset of their rash. This is to avoid them spreading measles to others.
What should you do?
- If you think your child has measles, let your GP practice know.
- Measles usually starts to get better in about a week.
- To make your child more comfortable, you may want to lower their temperature using paracetamol (calpol) or ibuprofen. If you've given your child one of these medications and they're still uncomfortable 2 hours later, you could try the other medication. If this works, you can alternate paracetamol and ibuprofen (every 2 to 3 hours), giving only 1 medicine at a time. Do not give more than the maximum daily dose of either medicine.
- However, remember that fever is a normal response that may help the body to fight infection. Paracetamol and ibuprofen will not get rid of it entirely. Paracetamol and Ibuprofen bring down the temperature but do not treat the infection. Whilst your child is unwell they will continue to get temperatures once the effects of the medicine has worn off.
- Avoid sponging your child. It doesn’t actually reduce your child’s temperature and may make your child shiver.
- Encourage your child to drink lots of fluids.
- If there are any crusts on your child's eyes, gently clean them using cotton wool soaked in warm water.
- Your child can spread the infection to others from the time their symptoms start until about 4 days after the rash appears.
- Children cannot go back to school or nursery until 4 days after the rash has started. They should also avoid contact with babies, pregnant women, people who have not had 2 doses of the MMR vaccine and people with weak immune systems.
- If you are pregnant and haven't received 2 doses of the MMR vaccine, or if there are any children in your family who are under 12 months old or any child who hasn't had 2 doses of the MMR vaccine, please inform your GP practice urgently. They might need immediate treatment to protect them from getting measles.
- If your child with measles has been in contact with someone who has a very weak immune system, let that person know about your child's measles. Ask them to contact their local specialty team, GP practice or NHS 111 urgently.
- Finally, make sure that you and your partner are up to date with your MMR vaccines before getting pregnant. Measles can be extremely severe during pregnancy and can harm your unborn baby.
Where should you seek help?
- Unless your child has red features (see above), try to stay away from public places including pharmacists, GP practices and A&E departments as your child may spread their infection to others.
- If your child has any of the above amber features (see above), urgently contact your GP or call NHS 111. Make sure you let them know if your child has not been vaccinated against measles (MMR vaccine).
- You should only call 999 or go to your nearest A&E department in critical or life threatening situations. Let a member of staff know as soon as you arrive if your child has not been vaccinated against measles (MMR vaccine).
What are the possible complications of measles infection?
Watch the following videos to see some of the possible consequences of measles infection:
For wear and tear, minor trips and everything in between.
Self-care
You can treat your child's very minor illnesses and injuries at home.
Some illnesses can be treated in your own home with support and advice from the services listed when required, using the recommended medicines and getting plenty of rest.
Sound advice
Children can recover from illness quickly but also can become more poorly quickly; it is important to seek further advice if a child's condition gets worse.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Pharmacists are experts in many aspects of healthcare and can offer advice on a wide range of long-term conditions and common illnesses such as coughs, colds and stomach upsets. You don’t need an appointment and many have private consultation areas, so they are a good first port of call. Your pharmacist will say if you need further medical attention.
Sound advice
- Visit a pharmacy if your child is ill, but does not need to see a GP.
- Remember that if your child's condition gets worse, you should seek further medical advice immediately.
- Help your child to understand - watch this video with them about going to the pharmacy.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns or to the Community Paediatricians or to the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact them by phoning your Health Visitor Team or local Children’s Centre.
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information watch the video: What does a health visitor do?
GPs assess, treat and manage a whole range of health problems. They also provide health education, give vaccinations and carry out simple surgical procedures. Your GP will arrange a referral to a hospital specialist should you need it.
Sound advice
You have a choice of service:
- Doctors/GPs can treat many illnesses that do not warrant a visit to A&E.
- Help your child to understand – watch this video with them about visiting the GP or going to a walk in centre
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
If you’re not sure which NHS service you need, call 111. An adviser will ask you questions to assess your symptoms and then give you the advice you need, or direct you straightaway to the best service for you in your area.
Sound advice
Use NHS 111 if you are unsure what to do next, have any questions about a condition or treatment or require information about local health services.
For information on common childhood illnesses go to What is wrong with my child?
A&E departments provide vital care for life-threatening emergencies, such as loss of consciousness, suspected heart attacks, breathing difficulties, or severe bleeding that cannot be stopped. If you’re not sure it’s an emergency, call 111 for advice.



